- The Hacker News: The Hacker News — most trusted and widely-acknowledged online cyber security news magazine with in-depth technical coverage for cybersecurity.
- Phrack Magazine: Digital hacking magazine.
- Metasploit: Find security issues, verify vulnerability mitigations & manage security assessments with Metasploit. Get the worlds best penetration testing software now.
- KitPloit: Leading source of Security Tools, Hacking Tools, CyberSecurity and Network Security.
- HackRead: HackRead is a News Platform that centers on InfoSec, Cyber Crime, Privacy, Surveillance, and Hacking News with full-scale reviews on Social Media Platforms.
- Packet Storm: Information Security Services, News, Files, Tools, Exploits, Advisories and Whitepapers.
- Exploit DB: An archive of exploits and vulnerable software by Offensive Security. The site collects exploits from submissions and mailing lists and concentrates them in a single database.
- Hacked Gadgets: A resource for DIY project documentation as well as general gadget and technology news.
Tuesday, June 30, 2020
Top 8 Websites to Learn How to Hack Like a Pro 2018
Thursday, June 11, 2020
Deepin Or UbuntuDDE
I'm sure nowadays many Deepin users are thinking in changing to UbuntuDDE, so let's explain some differences between both Linux distros.
1. Community
At least in the main telegram channel Deepin has more than 2.000 users, but UbuntuDDE is new in beta version and have about 500 users.
2. Boot
Despite de booting sound is the same in both distros, Deepin's animation is nicer than ubuntu's which uses a too bright background.

3. Default memory and CPU usage
The CPU usage is similar, but Deepin by default is using more processes, more network connections and more drivers than UbuntuDDE.


4. Workspaces
UbuntuDDE allows up to 7 workspaces meanwhile Deepin right now only allows 4.
Is not only more workspaces for UbuntuDDE, it's also the more eficient way to display them.


5. Software Versions
Deepin is based on Debian so the program versions on store and apt are old but stable, and can have problems with the old libraries installed on the system when compiling new software.
We can see below that Ubuntu's compiler version is quite new, the 9.3.0 which is quite well, but Deepin's version is 6.3.0.
Regarding the kernels, UbuntuDDE has the 5.4.0.21 and Deepin the 4.15.0-30, the libc in both systems is updated.
6. The store
Deepin's store is fast and polished and contain the main software, but and the UbuntuDDE
Conclussions
Deepin is the most used of both and it's the original one, but many users are trying the UbuntuDDE (which is beta for now) because the need of using recent versions, also the 4 workspaces on Deepin is another limitation for some Linux users. Probably Deepin v20 will overcome the limitations but the main decision is between Debian as base system or ubuntu, and for more users the trend in workstations is ubuntu.
Gallery
Related word
1. Community
At least in the main telegram channel Deepin has more than 2.000 users, but UbuntuDDE is new in beta version and have about 500 users.
2. Boot
Despite de booting sound is the same in both distros, Deepin's animation is nicer than ubuntu's which uses a too bright background.

3. Default memory and CPU usage
The CPU usage is similar, but Deepin by default is using more processes, more network connections and more drivers than UbuntuDDE.


4. Workspaces
UbuntuDDE allows up to 7 workspaces meanwhile Deepin right now only allows 4.
Is not only more workspaces for UbuntuDDE, it's also the more eficient way to display them.


5. Software Versions
Deepin is based on Debian so the program versions on store and apt are old but stable, and can have problems with the old libraries installed on the system when compiling new software.
We can see below that Ubuntu's compiler version is quite new, the 9.3.0 which is quite well, but Deepin's version is 6.3.0.
Regarding the kernels, UbuntuDDE has the 5.4.0.21 and Deepin the 4.15.0-30, the libc in both systems is updated.
6. The store
Deepin's store is fast and polished and contain the main software, but and the UbuntuDDE
Conclussions
Deepin is the most used of both and it's the original one, but many users are trying the UbuntuDDE (which is beta for now) because the need of using recent versions, also the 4 workspaces on Deepin is another limitation for some Linux users. Probably Deepin v20 will overcome the limitations but the main decision is between Debian as base system or ubuntu, and for more users the trend in workstations is ubuntu.
Gallery
Related word
HACKING PASSWORDS USING CREDENTIAL HARVESTER ATTACK
Everything over the internet is secured by the passwords. You need a login to do any stuff on any social or banking website. Passwords are the first security measure for these type of websites. So, I brought a tutorial on how to hack such sort of login passwords. This tutorial is based on credential harvester attack method. In which you will know about hacking passwords using credential harvester attack method.
HACKING PASSWORDS USING CREDENTIAL HARVESTER ATTACK
REQUIREMENTS
It's very simple and easy to follow. Before you start, you need the following things to work with.
- Kali Linux OS
- Target Website
STEPS TO FOLLOW
- Run the Kali Linux machine. If you have not Kali Linux installed, you can grab a free copy and install it as a virtual machine. You can learn more about Kali Linux VirtualBox installation.
- Sign in to Kali Linux by entering username root and password toor.
- As you'll sign in, navigate to the Applications > Social Engineering Tools > Social Engineering as shown in the following screenshot.
- Now you will see the different options. You have to choose Social Engineering Attacks by simply entering its number in the terminal. Once you do it, it will show a few options further. Simply choose Website Vector Attack by putting its number.
- Website vector attack will show up it's a different type of attacks. We are going to use Credential Harvester Attack.
- Choose the Site Clone option. As you do it, it will ask for your public IP address. Just open up a new terminal and type ifconfig. It'll show the public IP. Just copy it and paste in the previous terminal as shown in the following screenshots.
- After we do it. Enter the target website of which passwords you want to hack. Make sure to use a website that has username and password on the same page.
- All done now. As someone opens up the browser on the public IP we specified, it'll show up the website that we entered in the previous step. Now as someone enters their username or password, it will be captured in the terminal.
That's all. If you're not clear yet. You can watch the following complete video tutorial on how to do it.
More information
Microsoft Releases June 2020 Security Patches For 129 Vulnerabilities
Microsoft today released its June 2020 batch of software security updates that patches a total of 129 newly discovered vulnerabilities affecting various versions of Windows operating systems and related products. This is the third Patch Tuesday update since the beginning of the global Covid-19 outbreak, putting some extra pressure on security teams struggling to keep up with patch management
via The Hacker News
via The Hacker News
This article is the property of Tenochtitlan Offensive Security. Verlo Completo --> https://tenochtitlan-sec.blogspot.com
Related articlesBurpSuite Introduction & Installation
What is BurpSuite?
Burp Suite is a Java based Web Penetration Testing framework. It has become an industry standard suite of tools used by information security professionals. Burp Suite helps you identify vulnerabilities and verify attack vectors that are affecting web applications. Because of its popularity and breadth as well as depth of features, we have created this useful page as a collection of Burp Suite knowledge and information.
In its simplest form, Burp Suite can be classified as an Interception Proxy. While browsing their target application, a penetration tester can configure their internet browser to route traffic through the Burp Suite proxy server. Burp Suite then acts as a (sort of) Man In The Middle by capturing and analyzing each request to and from the target web application so that they can be analyzed.
Everyone has their favorite security tools, but when it comes to mobile and web applications I've always found myself looking BurpSuite . It always seems to have everything I need and for folks just getting started with web application testing it can be a challenge putting all of the pieces together. I'm just going to go through the installation to paint a good picture of how to get it up quickly.
BurpSuite is freely available with everything you need to get started and when you're ready to cut the leash, the professional version has some handy tools that can make the whole process a little bit easier. I'll also go through how to install FoxyProxy which makes it much easier to change your proxy setup, but we'll get into that a little later.
Requirements and assumptions:
Mozilla Firefox 3.1 or Later Knowledge of Firefox Add-ons and installation The Java Runtime Environment installed
Download BurpSuite from http://portswigger.net/burp/download.htmland make a note of where you save it.
on for Firefox from https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/foxyproxy-standard/
If this is your first time running the JAR file, it may take a minute or two to load, so be patient and wait.
Video for setup and installation.
You need to install compatible version of java , So that you can run BurpSuite.
$$$ Bug Bounty $$$
What is Bug Bounty ?
A bug bounty program, also called a vulnerability rewards program (VRP), is a crowdsourcing initiative that rewards individuals for discovering and reporting software bugs. Bug bounty programs are often initiated to supplement internal code audits and penetration tests as part of an organization's vulnerability management strategy.
Many software vendors and websites run bug bounty programs, paying out cash rewards to software security researchers and white hat hackers who report software vulnerabilities that have the potential to be exploited. Bug reports must document enough information for for the organization offering the bounty to be able to reproduce the vulnerability. Typically, payment amounts are commensurate with the size of the organization, the difficulty in hacking the system and how much impact on users a bug might have.
Mozilla paid out a $3,000 flat rate bounty for bugs that fit its criteria, while Facebook has given out as much as $20,000 for a single bug report. Google paid Chrome operating system bug reporters a combined $700,000 in 2012 and Microsoft paid UK researcher James Forshaw $100,000 for an attack vulnerability in Windows 8.1. In 2016, Apple announced rewards that max out at $200,000 for a flaw in the iOS secure boot firmware components and up to $50,000 for execution of arbitrary code with kernel privileges or unauthorized iCloud access.
While the use of ethical hackers to find bugs can be very effective, such programs can also be controversial. To limit potential risk, some organizations are offering closed bug bounty programs that require an invitation. Apple, for example, has limited bug bounty participation to few dozen researchers.
A bug bounty program, also called a vulnerability rewards program (VRP), is a crowdsourcing initiative that rewards individuals for discovering and reporting software bugs. Bug bounty programs are often initiated to supplement internal code audits and penetration tests as part of an organization's vulnerability management strategy.
Many software vendors and websites run bug bounty programs, paying out cash rewards to software security researchers and white hat hackers who report software vulnerabilities that have the potential to be exploited. Bug reports must document enough information for for the organization offering the bounty to be able to reproduce the vulnerability. Typically, payment amounts are commensurate with the size of the organization, the difficulty in hacking the system and how much impact on users a bug might have.
Mozilla paid out a $3,000 flat rate bounty for bugs that fit its criteria, while Facebook has given out as much as $20,000 for a single bug report. Google paid Chrome operating system bug reporters a combined $700,000 in 2012 and Microsoft paid UK researcher James Forshaw $100,000 for an attack vulnerability in Windows 8.1. In 2016, Apple announced rewards that max out at $200,000 for a flaw in the iOS secure boot firmware components and up to $50,000 for execution of arbitrary code with kernel privileges or unauthorized iCloud access.
While the use of ethical hackers to find bugs can be very effective, such programs can also be controversial. To limit potential risk, some organizations are offering closed bug bounty programs that require an invitation. Apple, for example, has limited bug bounty participation to few dozen researchers.
More articles
- Pentest Linux
- Pentest Meaning
- Pentest Os
- Hacker Ethic
- Pentest Uk
- What Hacking Is
- Pentestgeek
- Pentest Gear
- Hacking Box
- Pentestbox
- Pentest Lab Setup
- Hacker Software
- Pentest Devices
- Pentest Basics
- Hacking Site
- Pentest Blog
- How To Pentest A Website With Kali
- Hacking With Python
- Is Hacking Illegal
- Pentest Stages
Wednesday, June 10, 2020
Collection Of Pcap Files From Malware Analysis

Update: Feb 19. 2015
We have been adding pcaps to the collection so remember to check out the folder ( Pcap collection) for the recent pcaps.
I had a project to test some malicious and exploit pcaps and collected a lot of them (almost 1000) from various public sources. You can see them in the PUBLIC folder. The credits go to the authors of the pcaps listed in the name of each file. Please visit their blogs and sites to see more information about the pcaps, see their recent posts, and send them thanks. The public pcaps have no passwords on them.
Update:Dec 13. 2014
Despite rare updates of this post, we have been adding pcaps to the collection so remember to check out the folder ( Pcap collection (New link)) for the recent pcaps!
Update:Dec 31. 2013 - added new pcaps
I did some spring cleaning yesterday and came up with these malware and exploit pcaps. Such pcaps are very useful for IDS and signature testing and development, general education, and malware identification. While there are some online public sandboxes offering pcaps for download like Cuckoo or Anubis but looking for them is a tedious task and you cannot be totally sure the pcap is for the malware family supposedly analysed - in other words, if the sandbox says it is Zeus does not necessarily mean that it is.
I found some good pcap repositories here (http://www.netresec.com/?page=PcapFiles) but there are very few pcaps from malware.
These are from identified and verified (to the best of my knowledge and belief - email me if you find errors) malware samples.
All of them show the first stage with the initial callback and most have the DNS requests as well. A few pcaps show extended malware runs (e.g. purplehaze pcap is over 500mb).
Most pcaps are mine, a few are from online sandboxes, and one is borrowed from malware.dontneedcoffee.com. That said, I can probably find the corresponding samples for all that have MD5 listed if you really need them. Search contagio, some are posted with the samples.
Each file has the following naming convention:
BIN [RTF, PDF] - the filetype of the dropper used, malware family name, MD5, and year+month of the malware analysis.
I will be adding more pcaps in the future. Please donate your pcaps from identified samples, I am sure many of you have.
Thank you
Download
 Download all together or separately.
Download all together or separately.All pcaps archives have the same password (same scheme), email me if you need it. I tried posting it without any passwords and pass infected but they get flagged as malware. Modern AV rips though zips and zips with the pass 'infected' with ease.
APT PCAPS
- 2012-12-31 BIN_Xinmic_8761F29AF1AE2D6FACD0AE5F487484A5-pcap
- 2013-09-08 BIN_TrojanPage_86893886C7CBC7310F7675F4EFDE0A29-pcap
- 2013-09-08 BIN_Darkcomet_DC98ABBA995771480AECF4769A88756E-pcap
- 2013-09-02 8202_tbd_ 6D2C12085F0018DAEB9C1A53E53FD4D1-pcap
- 2013-09-02 BIN_8202_6d2c12085f0018daeb9c1a53e53fd4d1-pcap
- 2013-09-02 BIN_Vidgrab_6fd868e68037040c94215566852230ab-pcap
- 2013-09-02 BIN_PlugX_2ff2d518313475a612f095dd863c8aea-pcap
- 2013-09-02 BIN_Taidoor_46ef9b0f1419e26f2f37d9d3495c499f-pcap
- 2013-09-02 BIN_Vidgrab_660709324acb88ef11f71782af28a1f0-pcap
- 2013-09-02 BIN_Gh0st-gif_f4d4076dff760eb92e4ae559c2dc4525-pcap.zip
- 2013-07-15 BIN_Taleret.E_5328cfcb46ef18ecf7ba0d21a7adc02c.pcap
- 2013-05-14 BIN_Mediana_0AE47E3261EA0A2DBCE471B28DFFE007_2012-10.pcap
- 2013-05-14 BIN_Hupigon_8F90057AB244BD8B612CD09F566EAC0C
- 2013-05-14 BIN_LetsGo_yahoosb_b21ba443726385c11802a8ad731771c0_2011-07-19
- 2013-05-13 BIN_IXESHE_0F88D9B0D237B5FCDC0F985A548254F2-2013-05-pcap
- 2013-05-06 BIN_DNSWatch_protux_4F8A44EF66384CCFAB737C8D7ADB4BB8_2012-11-pcap
- 2013-05-06 BIN_9002_D4ED654BCDA42576FDDFE03361608CAA_2013-01-30-pcap
- 2013-05-06 BIN_BIN_RssFeeder_68EE5FDA371E4AC48DAD7FCB2C94BAC7-2012-06-pcap (not a common name, see the traffic ssheet http://bit.ly/maltraffic )
- 2013-04-30 BIN_MSWab_Yayih_FD1BE09E499E8E380424B3835FC973A8_us-pcap
- 2013-04-29 BIN_LURK_AF4E8D4BE4481D0420CCF1C00792F484_20120-10-pcap
- 2013-04-29 BIN_XTremeRAT_DAEBFDED736903D234214ED4821EAF99_2013-04-13-pcap
- BIN_Enfal_Lurid_0fb1b0833f723682346041d72ed112f9_2013-01.pcap
- BIN_Gh0st_variant-v2010_B1D09374006E20FA795B2E70BF566C6D_2012-08.pcap
- BIN_Likseput_E019E37F19040059AB5662563F06B609_2012-10.pcap
- BIN_Nettravler_1f26e5f9b44c28b37b6cd13283838366.pcap
- BIN_Nettravler_DA5832657877514306EDD211DEF61AFE_2012-10.pcap
- BIN_Sanny-Daws_338D0B855421867732E05399A2D56670_2012-10.pcap
- BIN_Sofacy_a2a188cbf74c1be52681f998f8e9b6b5_2012-10.pcap
- BIN_Taidoor_40D79D1120638688AC7D9497CC819462_2012-10.pcap
- BIN_TrojanCookies_840BD11343D140916F45223BA05ABACB_2012_01.pcap
- PDF_CVE-2011-2462_Pdf_2011-12.pcap
- RTF_Mongall_Dropper_Cve-2012-0158_C6F01A6AD70DA7A554D48BDBF7C7E065_2013-01.pcap
- OSX_DocksterTrojan.pcap
CRIMEWARE PCAPS
- 2013-11-12_BIN_ChePro_2A5E5D3C536DA346849750A4B8C8613A-1.pcap
- 2013-10-15_BIN_cryptolocker_9CBB128E8211A7CD00729C159815CB1C.pcap
- 2013-09-20_BIN_Lader-dlGameoverZeus_12cfe1caa12991102d79a366d3aa79e9.pcap
- 2013-09-08 BIN_Tijcont_845B0945D5FE0E0AAA16234DC21484E0-pcap
- 2013-09-08 BIN_Kelihos_C94DC5C9BB7B99658C275B7337C64B33-pcap.zip
- 2013-08-19 BIN_Nitedrem_508af8c499102ad2ebc1a83fdbcefecb-pcap
- 2013-08-17 BIN_sality_CEAF4D9E1F408299144E75D7F29C1810-pcap
- 2013-08-15 BIN_torpigminiloader-pcap.zip
- 2013-13-08 EK_popads_109.236.80.170_2013-08-13.pcap
- 2013-11-08 BIN_Alinav5.3_4C754150639AA3A86CA4D6B6342820BE.pcap
- 2013-08-08 BIN_BitcoinMiner_F865C199024105A2FFDF5FA98F391D74-pcap
- 2013-08-07 BIN_ZeroAccess_Sirefef_C2A9CCC8C6A6DF1CA1725F955F991940_2013-08-pcap
- 2013-07-05 BIN_Kuluoz-Asprox_9F842AD20C50AD1AAB41F20B321BF84B
- 2013-05-31 Wordpress-Mutopy_Symmi_20A6EBF61243B760DD65F897236B6AD3-2pcap.pcap
- 2013-05-15 BIN_Zeus_b1551c676a54e9127cd0e7ea283b92cc-2012-04.pcap
- 2013-05-15 BIN_Gypthoy_3EE49121300384FF3C82EB9A1F06F288-2013-05.pcap
- 2013-05-12 BIN_PassAlert_B4A1368515C6C39ACEF63A4BC368EDB2-2013-05-13
- 2013-05-12 BIN_HorstProxy_EFE5529D697174914938F4ABF115F762-2013-05-13-pcap
- 2013-05-12 BIN_Bitcoinminer_12E717293715939C5196E604591A97DF-2013-05-12-pcap
- 2013-05-07 BIN_ZeroAccess_Sirefef_29A35124ABEAD63CD8DB2BBB469CBC7A_2013-05-pcapc
- 2013-05-05 BIN_PowerLoader_4497A231DA9BD0EEA327DDEC4B31DA12_2013-05-pcap
- 2013-05-05 BIN_GameThief_ECBA0FEB36F9EF975EE96D1694C8164C_2013-03-pcap
- 2013-05-05 BIN_PowerLoader_4497A231DA9BD0EEA327DDEC4B31DA12_2013-05-pcap
- 2013-04-27 EK_BIN_Blackhole_leadingto_Medfos_0512E73000BCCCE5AFD2E9329972208A_2013-04-pcap
- 2013-04-26 -- BIN_Citadel_3D6046E1218FB525805E5D8FDC605361-2013-04-samp
- BIN_CitadelPacked_2012-05.pcap
- BIN_CitadelUnpacked_2012-05.pcap
- BIN_Cutwail_284Fb18Fab33C93Bc69Ce392D08Fd250_2012-10.pcap
- BIN_Darkmegi_2012-04.pcap
- BIN_DarknessDDoS_v8g_F03Bc8Dcc090607F38Ffb3A36Ccacf48_2011-01.pcap-
- BIN_dirtjumper_2011-10.pcap
- BIN_DNSChanger_2011-12.pcap
- BIN_Drowor_worm_0f015bb8e2f93fd7076f8d178df2450d_2013-04.pcap
- BIN_Googledocs_macadocs_2012-12.pcap
- BIN_Imaut_823e9bab188ad8cb30c14adc7e67066d.pcap
- BIN_IRCbot_c6716a417f82ccedf0f860b735ac0187_2013-04.pcap
- BIN_Kelihos_aka_Nap_0feaaa4adc31728e54b006ab9a7e6afa.pcap
- BIN_LoadMoney_MailRu_dl_4e801b46068b31b82dac65885a58ed9e_2013-04 .pcap
- BIN_purplehaze-2012-01.pcap
- BIN_ponyloader_470a6f47de43eff307a02f53db134289.pcap
- BIN_Ramnitpcap_2012-01.pcap
- BIN_Reedum_0ca4f93a848cf01348336a8c6ff22daf_2013-03.pcap
- BIN_SpyEye_2010-02.pcap
- BIN_Stabuniq_F31B797831B36A4877AA0FD173A7A4A2_2012-12.pcap
- BIN_Tbot_23AAB9C1C462F3FDFDDD98181E963230_2012-12.pcap
- BIN_Tbot_2E1814CCCF0C3BB2CC32E0A0671C0891_2012-12.pcap
- BIN_Tbot_5375FB5E867680FFB8E72D29DB9ABBD5_2012-12.pcap
- BIN_Tbot_A0552D1BC1A4897141CFA56F75C04857_2012-12.pcap
- BIN_Tbot_FC7C3E087789824F34A9309DA2388CE5_2012-12.pcap
- BIN_Tinba_2012-06.pcap
- BIN_Vobfus_634AA845F5B0B519B6D8A8670B994906_2012-12.pcap
- BIN_Xpaj_2012-05.pcap
- BIN_ZeroAccess_3169969E91F5FE5446909BBAB6E14D5D_2012-10.pcap
- BIN_ZeusGameover_2012-02.pcap
- BIN_Zeus_2010-12.pcap
- EK_Blackholev1_2012-03.pcap
- EK_Blackholev1_2012-08.pcap
- EK_Blackholev2_2012-09.pcap
- EK_Blackhole_Java_CVE-2012-4681_2012-08.pcap
- EK_Phoenix_2012-04.pcap
- EK_Smokekt150(Malwaredontneedcoffee)_2012-09.pcap - credit malware.dontneedcoffee.com
Related links
5 Free Online Courses To Learn Artificial Intelligence
We are living in the era of fourth industrial revolution(4IR), where Artificial intelligence has a significant role to play. This 4IR technology embedded within societies and even into the human body. From Computer enthusiasts to common people, everyone should be aware and learn this breakthrough technology.
We think about gigantic Robots from Transformers when we hear about Artificial Intelligence(AI) which is a fiction in the past but a fact today, capable of transforming the whole tech world. The field of AI consists of more than Robots such as personal assistants, self-driving cars, apprenticeship learning, behavior cloning and so on. To learn about this advanced technology, thanks to the online learning resources which offers great content to get started with artificial intelligence.
Here are the 5 free e-learning courses on Artificial Intelligence
1. UC Berkeley CS188 Intro to AI
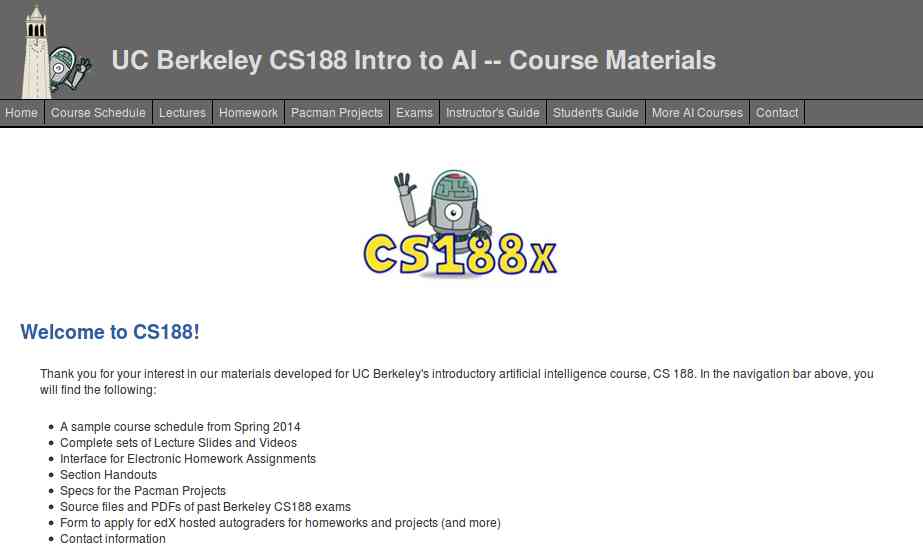
Get started with UC Berkeley AI course, this course is absolutely for beginners who are unaware of Artificial intelligence. It doesn't need any prior computer knowledge to know about AI. UC Berkeley allows anyone to learn this course for free. This course is systematically presented and consists of the following:
- Course Schedule
- Complete sets of Lecture Slides and Videos
- Interface for Electronic Homework Assignments
- Section Handouts
- Specs for the Pacman Projects
- Source files and PDFs of past Berkeley CS188 exams
- Form to apply for edX hosted autograders for homework and projects (and more)
- Contact information
Aside from this, you can also browse the following courses as well from UC Berkeley that are part of AI course:
- Machine Learning: CS189, Stat154
- Intro to Data Science: CS194-16
- Probability: EE126, Stat134
- Optimization: EE127
- Cognitive Modeling: CogSci131
- Machine Learning Theory: CS281A, CS281B
- Vision: CS280
- Robotics: CS287
- Natural Language Processing: CS288
2. Artificial Intelligence: Principles and Techniques
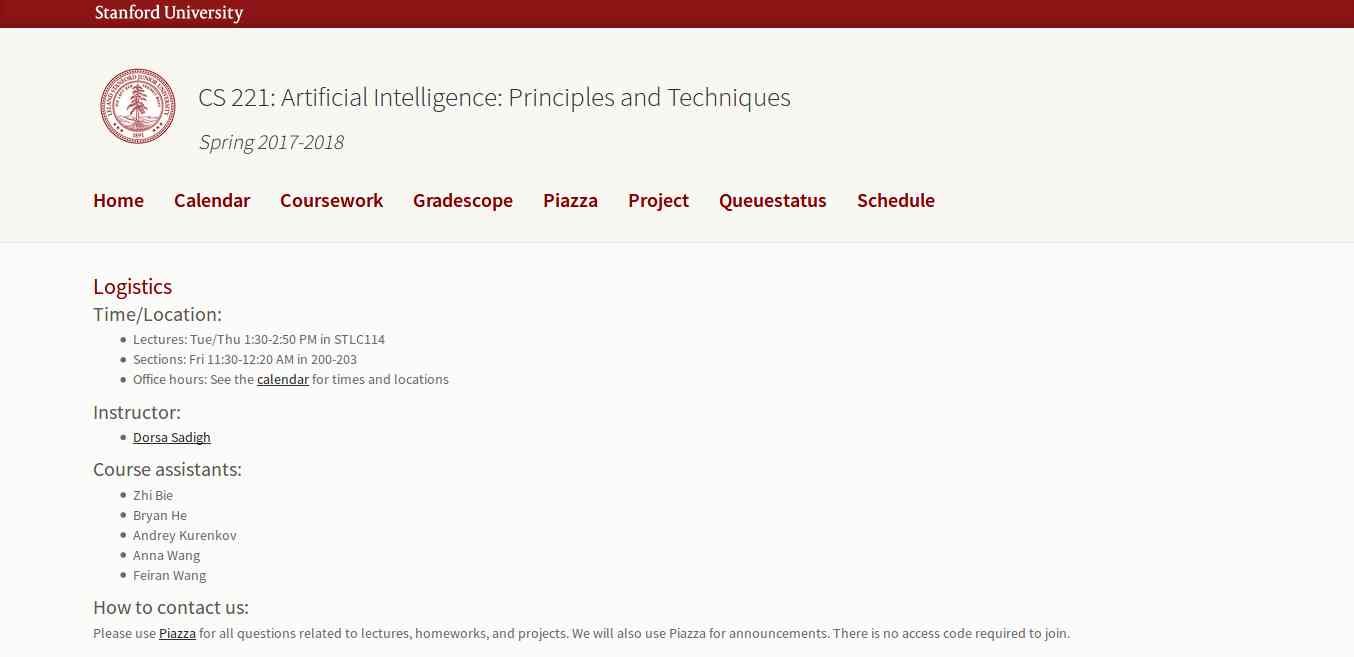
This course is offered by Stanford with great content that includes topics, videos, assignments, projects, and exams. The whole course mainly focuses on the complex real-world problems and try to find similarity between web search, speech recognition, face recognition, machine translation, autonomous driving, and automatic scheduling. Here you will learn the foundational principles of AI and implement some the AI systems. The goal of this course is to help you tackle the real-world situations with the help of AI tools. So, it is the best for the beginner to get started with AI.
3. Learn with GOOGLE AI
Who will dislike the course from Google? absolutely no one. This company is one of the early adopters of AI has a lot to offer to learners. Learn with Google AI is an education platform for people at all experience levels, it is free to access and browse content. The education resources provided by Google is from the machine learning experts of the company. These resources are the collections of lessons, tutorials, and Hands-on exercises that help you start learning, building, and problem-solving.
4. MIT 6.S094: Deep Learning for Self-Driving Cars
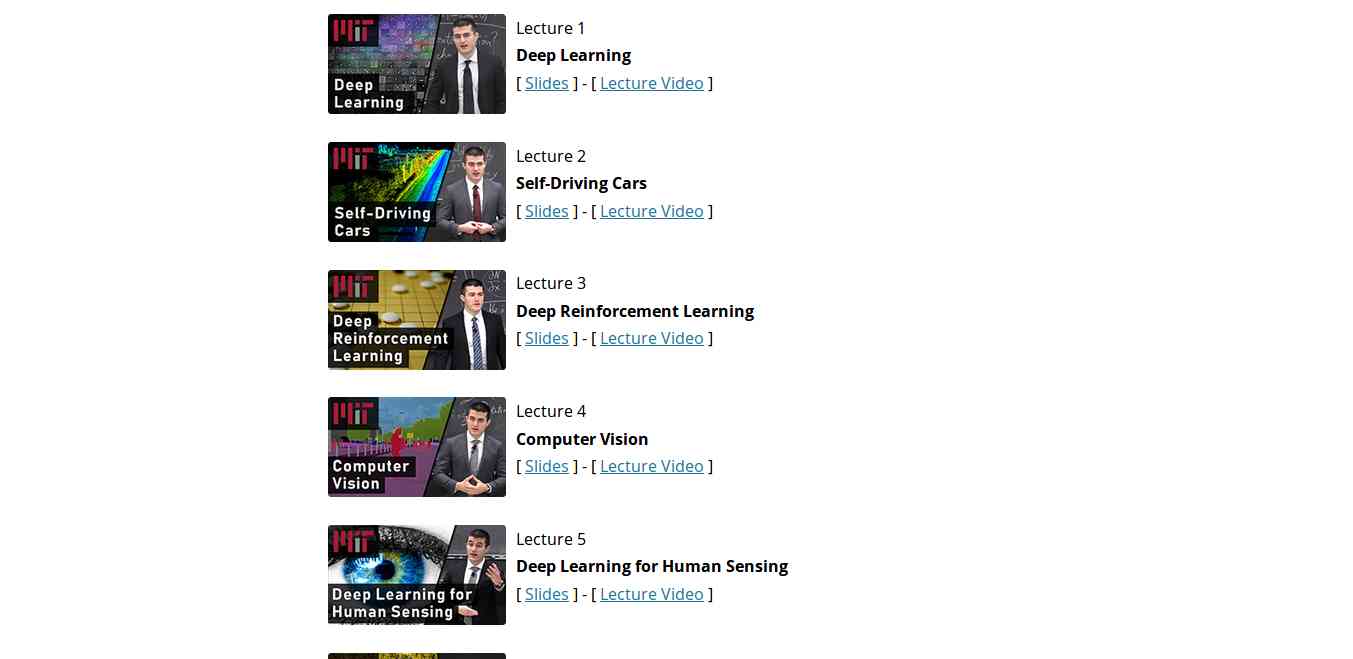
This course gives the practical overview of Deep Learning and AI. It is the course for beginners, also for the people who are getting started with Machine Learning. The course also offers a lot of benefits to the experienced and advanced researchers in the field deep learning. This MIT's course takes people into the journey of Deep Learning with the applied theme of building Self-Driving cars. However, the course also offers slides and videos to engage the learners.
5. Fundamentals of Deep Learning for Computer Vision
This course is offered by Nvidia and Nvidia Deep learning Institute. Computer Vision is one of the disciplines of AI that acquire, analyze, process, and understand images. The course is completely free and everyone who is enthusiast about AI can access and learn the course. It is a hands-on course that able to provide basics of deep learning and deployment of neural networks. With this. you will also learn the following:
- Identify the ingredients required to start a Deep Learning project.
- Train a deep neural network to correctly classify images it has never seen before.
- Deploy deep neural networks into applications.
- Identify techniques for improving the performance of deep learning applications.
- Assess the types of problems that are candidates for deep learning.
- Modify neural networks to change their behavior.
Related news
Vlang Binary Debugging
Why vlang? V is a featured, productive, safe and confortable language highly compatible with c, that generates neat binaries with c-speed, the decompilation also seems quite clear as c code.
https://vlang.io/
After open the binary with radare in debug mode "-d" we proceed to do the binary recursive analysis with "aaaa" the more a's the more deep analys.
The function names are modified when the binary is crafted, if we have a function named hello in a module named main we will have the symbol main__hello, but we can locate them quicly thanks to radare's grep done with "~" token in this case applied to the "afl" command which lists all the symbols.
Being in debug mode we can use "d*" commands, for example "db" for breakpointing the function and then "dc" to start or continue execution.
Let's dissasemble the function with "pD" command, it also displays the function variables and arguments as well, note also the xref "call xref from main"
Let's take a look to the function arguments, radare detect's this three 64bits registers used on the function.
Actually the function parameter is rsi that contains a testing html to test the href extraction algorithm.
The string structure is quite simple and it's plenty of implemented methods.
With F8 we can step over the code as we were in ollydbg on linux.
Note the rip marker sliding into the code.
We can recognize the aray creations, and the s.index_after() function used to find substrings since a specific position.
If we take a look de dissasembly we sill see quite a few calls to tos3() functions.
Those functions are involved in string initialization, and implements safety checks.
In this case I have a crash in my V code and I want to know what is crashing, just continue the execution with "dc" and see what poits the rip register.
In visual mode "V" we can see previous instructions to figure out the arguments and state.
We've located the crash on the substring operation which is something like "s2 := s1[a..b]" probably one of the arguments of the substring is out of bounds but luckily the V language has safety checks and is a controlled termination:
Switching the basic block view "space" we can see the execution flow, in this case we know the loops and branches because we have the code but this view also we can see the tos3 parameter "href=" which is useful to locate the position on the code.
When it reach the substr, we can see the parameters with "tab" command.
Looking the implementation the radare parameter calculation is quite exact.
Let's check the param values:
so the indexes are from 0x0e to 0x24 which are inside the buffer, lets continue to next iteration,
if we set a breakpoint and check every iteration, on latest iteration before the crash we have the values 0x2c to 0x70 with overflows the buffer and produces a controlled termination of the v compiled process.
Related posts
https://vlang.io/
After open the binary with radare in debug mode "-d" we proceed to do the binary recursive analysis with "aaaa" the more a's the more deep analys.
The function names are modified when the binary is crafted, if we have a function named hello in a module named main we will have the symbol main__hello, but we can locate them quicly thanks to radare's grep done with "~" token in this case applied to the "afl" command which lists all the symbols.
Being in debug mode we can use "d*" commands, for example "db" for breakpointing the function and then "dc" to start or continue execution.
Let's dissasemble the function with "pD" command, it also displays the function variables and arguments as well, note also the xref "call xref from main"
Let's take a look to the function arguments, radare detect's this three 64bits registers used on the function.
Actually the function parameter is rsi that contains a testing html to test the href extraction algorithm.
The string structure is quite simple and it's plenty of implemented methods.
With F8 we can step over the code as we were in ollydbg on linux.
Note the rip marker sliding into the code.
We can recognize the aray creations, and the s.index_after() function used to find substrings since a specific position.
If we take a look de dissasembly we sill see quite a few calls to tos3() functions.
Those functions are involved in string initialization, and implements safety checks.
- tos(string, len)
- tos2(byteptr)
- tos3(charptr)
In this case I have a crash in my V code and I want to know what is crashing, just continue the execution with "dc" and see what poits the rip register.
In visual mode "V" we can see previous instructions to figure out the arguments and state.
We've located the crash on the substring operation which is something like "s2 := s1[a..b]" probably one of the arguments of the substring is out of bounds but luckily the V language has safety checks and is a controlled termination:
Switching the basic block view "space" we can see the execution flow, in this case we know the loops and branches because we have the code but this view also we can see the tos3 parameter "href=" which is useful to locate the position on the code.
When it reach the substr, we can see the parameters with "tab" command.
Looking the implementation the radare parameter calculation is quite exact.
Let's check the param values:
so the indexes are from 0x0e to 0x24 which are inside the buffer, lets continue to next iteration,
if we set a breakpoint and check every iteration, on latest iteration before the crash we have the values 0x2c to 0x70 with overflows the buffer and produces a controlled termination of the v compiled process.
Related posts
- Pentest Online Course
- Pentest Tools Github
- Pentest Azure
- Hacking Images
- Pentest Reporting Tool
- Hacker News
- Pentest Azure
- Pentest Framework
- Pentest Training
- Pentest Tools Framework
- Pentest Uk
- Pentest With Kali
- Pentestlab
- Hacking Simulator
- Hacker Language
- Pentest Plus
- Hacker Typer
- Hacker0Ne
- Pentest With Metasploit
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)





























